In recent years, blockchain technology has emerged as a disruptive force across various industries, promising transparency, security, and decentralization. One sector that has been particularly impacted is the gaming industry. Blockchain game development has opened up new possibilities for game creators, players, and investors. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of blockchain game development, its potential, and how it is reshaping the gaming landscape.
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain
Before we delve into the exciting world of blockchain game development, it’s essential to grasp the core concepts of blockchain technology.
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed and decentralized ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It consists of a chain of blocks, each containing a list of transactions. Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes immutable, and the information it holds is secure and transparent.
Key Characteristics of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers. No single entity or organization has control over the entire system.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent and auditable history of actions.
- Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure data. Once data is added to the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to alter or delete.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts enable automation of tasks when predefined conditions are met.
Blockchain and the Gaming Industry

The gaming industry has long been a playground for innovation, with technology pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Blockchain technology has introduced a new dimension to gaming, creating opportunities and solving long-standing challenges.
Benefits of Blockchain in Gaming
- Ownership and Scarcity: Blockchain enables true ownership of in-game assets. Items or characters in a blockchain game are represented as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), giving players full control and ownership of their digital possessions.
- Interoperability: Blockchain games can have interoperable assets, allowing items from one game to be used in another. This opens up the potential for a shared gaming economy.
- Transparency: Blockchain records every transaction and in-game action, ensuring fairness and transparency. Players can verify the rarity of items and the integrity of the game’s mechanics.
- Monetization: Game developers can implement various monetization strategies using blockchain, such as NFT sales, token rewards, and play-to-earn mechanics.
- Community Engagement: Blockchain games often involve their communities in decision-making processes, making players more invested in the success of the game.
Challenges in Blockchain Game Development
While blockchain offers immense potential, it also presents unique challenges for game developers:
- Scalability: Blockchain networks like Ethereum face scalability issues, causing high gas fees and slow transaction times. This can hinder the user experience in blockchain games.
- User Onboarding: Users unfamiliar with blockchain technology may find it intimidating to get started. Simplifying the onboarding process is crucial for mass adoption.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape for blockchain games and NFTs is still evolving. Developers need to navigate these uncertainties carefully.
The Rise of NFTs in Gaming
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are a cornerstone of blockchain game development. NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of in-game items, characters, and collectibles. The advent of NFTs has transformed the gaming industry in several ways:
- True Ownership: With NFTs, players have verifiable ownership of their in-game assets. This has led to a thriving secondary market where players can buy, sell, and trade their digital possessions.
- Digital Collectibles: NFTs have given rise to the concept of digital collectibles. Gamers are now collecting and showcasing rare items and NFT-based art.
- Play-to-Earn: Some blockchain games adopt a play-to-earn model, where players can earn valuable NFTs by participating in the game. This aligns the interests of developers and players, fostering a vibrant gaming ecosystem.
Popular Blockchain Games
Blockchain game development has witnessed the emergence of various popular games that demonstrate the potential of the technology. Let’s take a closer look at a few of these titles:
1. Axie Infinity
Axie Infinity is a play-to-earn blockchain game where players collect, breed, and battle fantasy creatures called Axies. Players can earn cryptocurrency by participating in battles and marketplace activities. The game has gained widespread attention for its unique economic model.
2. Decentraland
Decentraland is a decentralized virtual world built on the Ethereum blockchain. Users can buy, sell, and develop parcels of land in the virtual universe. This project showcases the potential of blockchain technology in creating user-owned virtual spaces.
3. CryptoKitties
CryptoKitties was one of the earliest NFT-based games that allowed players to buy, breed, and trade virtual cats. It introduced the concept of digital collectibles and NFTs to a broader audience.
4. The Sandbox
The Sandbox is a user-generated content platform that empowers creators to design, build, and monetize their gaming experiences. It utilizes NFTs to represent in-game assets, making it an excellent example of blockchain’s impact on user-generated content.
Getting Started with Blockchain Game Development
If you’re a game developer or enthusiast looking to venture into blockchain game development, here are some essential steps to get started:
- Learn About Blockchain Technology: Gain a solid understanding of blockchain technology, its use cases, and how it can be applied in gaming.
- Choose the Right Blockchain: Select a blockchain platform that suits your game’s requirements. Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Flow are popular choices.
- Develop Smart Contracts: Learn how to create and deploy smart contracts that manage in-game assets and transactions.
- Work with NFTs: Understand NFT standards like ERC-721 and ERC-1155 and how to integrate them into your game.
- User Onboarding: Simplify the user onboarding process, making it easy for players to interact with blockchain features.
- Community Building: Engage with the blockchain gaming community and seek feedback on your project. Collaboration and networking can be invaluable.
- Test and Iterate: Test your game thoroughly and iterate based on user feedback. Improving the user experience is key to a successful blockchain game.
- Security and Compliance: Ensure that your game complies with legal and security requirements, as blockchain games often involve real-world value.
Conclusion
Blockchain game development represents an exciting intersection of two innovative worlds: blockchain technology and gaming. The potential to provide players with true ownership, unique in-game assets, and new economic models makes blockchain games a promising frontier. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more groundbreaking developments in this space.
Creating Web3-Powered Games: A Step-by-Step Guide
In the previous article, we introduced you to the exciting world of blockchain game development and its potential to revolutionize the gaming industry. We discussed the basics of blockchain technology, the rise of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and popular blockchain games. Now, let’s take a deeper dive into the technical aspects of creating web3-powered games, exploring how blockchain and decentralized technologies can be integrated into game development.
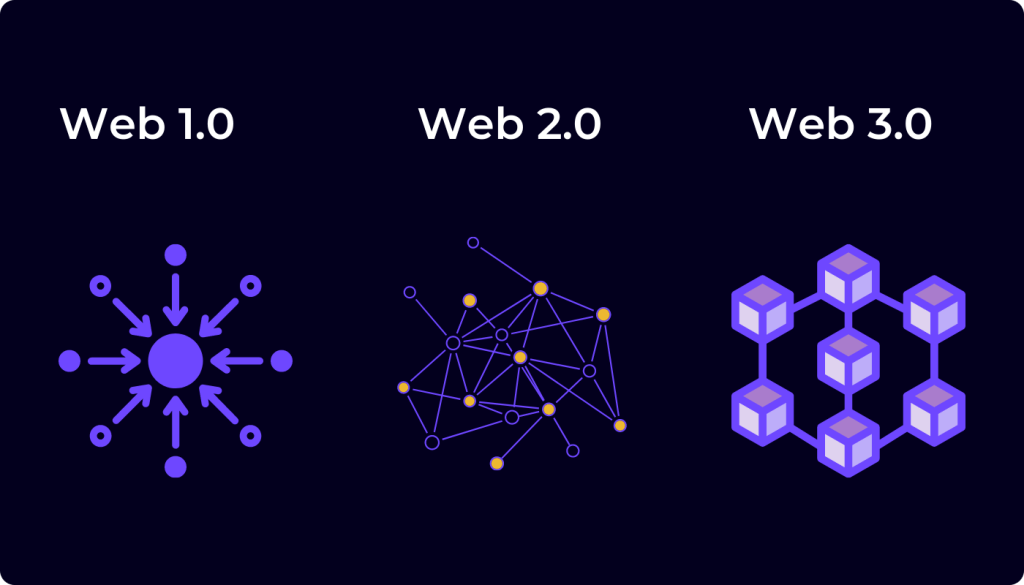
The Foundations of Web3-Powered Games
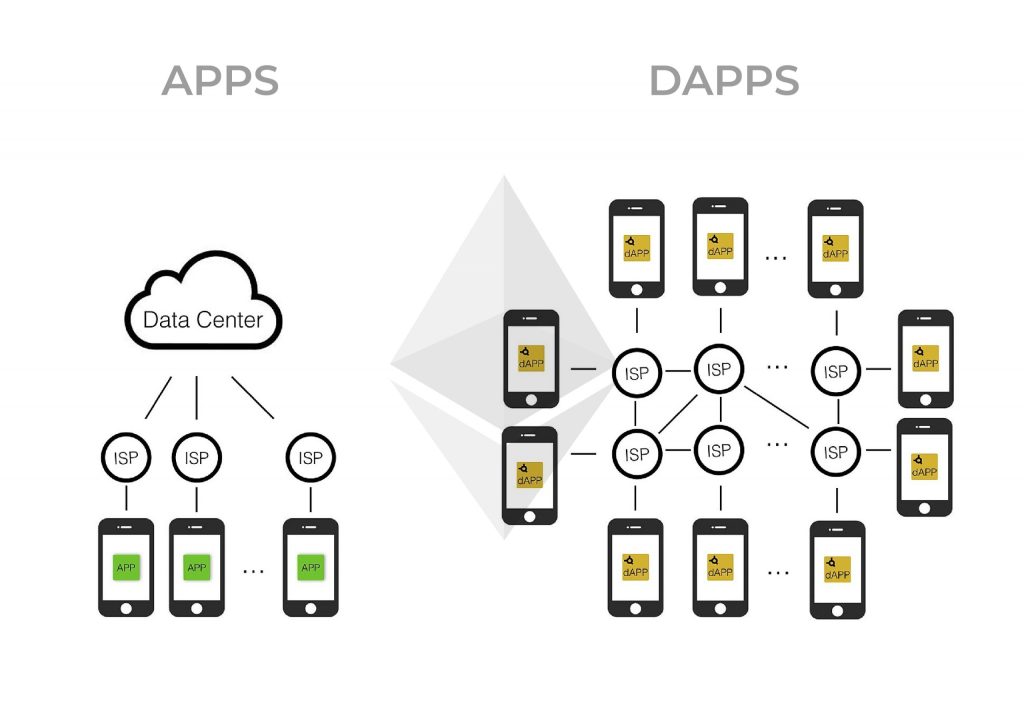
Web3, often referred to as “Web3.0,” represents a new paradigm in internet technology that emphasizes decentralization, user ownership, and interoperability. It is closely linked to blockchain technology and decentralized applications (dApps). To create web3-powered games, you’ll need to understand the core components of this emerging ecosystem.
1. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is the backbone of web3-powered games. It provides the infrastructure for secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions and asset ownership. Key aspects of blockchain technology include:
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts that automate in-game mechanics, transactions, and asset management.
- NFTs: Non-fungible tokens represent unique in-game assets, giving players true ownership.
- Decentralization: Games run on a network of nodes, ensuring no single entity has control.
2. Decentralized Platforms
Web3 games are often built on decentralized platforms that support smart contracts and NFTs. Some popular platforms include:
- Ethereum: The leading platform for decentralized applications, known for its robust ecosystem and NFT standards.
- Binance Smart Chain: Offers faster and cheaper transactions compared to Ethereum, making it a popular choice for some games.
- Flow: Designed for high-performance dApps and games, Flow offers unique advantages for blockchain gaming.
3. Web3 Tools and Development Frameworks
To develop web3-powered games, you’ll need to work with a set of tools and development frameworks designed for blockchain and smart contract development. Some essential tools include:
- Truffle: A development environment, testing framework, and asset pipeline for Ethereum.
- Hardhat: A development environment for Ethereum that supports smart contract development and testing.
- Remix: An online IDE for smart contract development with a built-in Solidity compiler.
- Metamask: A browser extension wallet that enables users to interact with dApps seamlessly.
4. Solidity and Smart Contracts
Solidity is the most commonly used programming language for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum platform. To create web3 games, developers should have a good grasp of Solidity, as it forms the core of in-game logic, NFT creation, and transactions.
Steps to Create a Web3-Powered Game
Now that you have a foundational understanding of web3 and its components, let’s dive into the steps required to create a web3-powered game. We’ll walk you through the process, from concept to deployment.
1. Conceptualize Your Game
Before you start coding, you need a clear game concept. Decide on the game’s genre, mechanics, and how blockchain and web3 elements will enhance the player experience. Consider the following:
- What in-game assets will be represented as NFTs?
- How will players earn or trade these assets?
- Will your game have a play-to-earn model, and if so, how will it work?
2. Select the Right Blockchain
Choose the blockchain platform that aligns with your game’s requirements. Consider factors like transaction speed, cost, and community support. Ethereum is a popular choice for its wide adoption, but other blockchains like Binance Smart Chain and Flow may offer unique advantages for your game.
3. Design and Develop Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are at the heart of your web3-powered game. Design smart contracts that manage in-game assets, transactions, and mechanics. Here are some key steps in this process:
- Define the functions and rules of your smart contracts.
- Implement NFT standards like ERC-721 or ERC-1155 to represent in-game assets.
- Write and test your smart contracts using development frameworks like Truffle or Hardhat.
4. Integrate Web3 Features
Integrate web3 features into your game to enable blockchain interactions and transactions. This involves:
- Implementing a wallet solution like Metamask to allow players to interact with your game.
- Enabling NFT creation and ownership, ensuring players have true ownership of in-game assets.
- Setting up transactions for in-game actions and asset transfers.
5. User Onboarding and Wallet Integration
Ensure that the onboarding process for users is smooth and user-friendly. Integrate a wallet solution like Metamask into your game and provide clear instructions for players who may be new to web3 technology.
6. Testing and Iteration
Thoroughly test your game to identify and fix any bugs, security vulnerabilities, or usability issues. Engage with the gaming community and gather feedback for improvements. Web3-powered games often rely on player trust and involvement, so community feedback is invaluable.
7. Security and Compliance
Given the real-world value associated with in-game assets and transactions, it’s essential to prioritize security and compliance. Ensure your game complies with legal regulations and best practices in blockchain security.
8. Deployment
Once your game is thoroughly tested and polished, it’s time to deploy it on the chosen blockchain. This involves deploying your smart contracts, setting up user interfaces, and making the game accessible to players.
9. Community Building and Marketing
Building a strong community around your web3-powered game is crucial for its success. Engage with players, answer their questions, and create marketing campaigns to promote your game within the blockchain gaming community.
10. Monetization Strategies
Consider how you will monetize your web3-powered game. This may include selling NFTs, offering in-game purchases, or implementing a play-to-earn model. Be transparent with your players about your monetization strategies.
Web3-Powered Game Examples
Let’s explore a few examples of web3-powered games that showcase the potential of blockchain integration in gaming:
1. Axie Infinity
Axie Infinity, mentioned in the previous article, is a prime example of a web3-powered game. It features NFT-based creatures, battles, and a vibrant in-game economy. Players can earn cryptocurrency by participating in battles and selling NFTs.
2. CryptoKaiju
CryptoKaiju offers collectible, customizable, and tradable physical toys. Each toy has a unique digital identity stored on the blockchain as an NFT. Players can collect and trade these toys, blurring the line between physical and digital collectibles.
3. Blankos Block Party
Blankos Block Party is a blockchain-enabled game where players collect and customize vinyl toy characters. These characters are represented as NFTs, allowing players to truly own and trade their in-game assets.
Challenges and Considerations
Web3-powered game development comes with its own set of challenges and considerations:
- Scalability: Blockchain networks like Ethereum may suffer from scalability issues, leading to high gas fees and slower transaction times. Developers should consider solutions like Layer 2 scaling solutions or alternative blockchains.
- User Education: Onboarding players who may not be familiar with blockchain technology can be a hurdle. Clear tutorials and user-friendly interfaces are essential.
- Regulatory Landscape: The regulatory environment for blockchain games and NFTs is evolving. Developers must stay informed about legal requirements and compliance.
- Security: The security of smart contracts and in-game assets is paramount. Auditing and thorough testing are essential to protect player investments.
Conclusion
Creating web3-powered games represents a dynamic intersection of gaming and blockchain technology. It offers players true ownership of in-game assets, unique economic models, and exciting opportunities for developers and players alike. In this article, we’ve walked you through the steps involved in developing a web3-powered game, from conceptualization to deployment.
From DApps to Enterprise Solutions: Blockchain Development for Business
In the previous articles, we explored the fascinating world of blockchain game development and web3-powered games. We discussed how blockchain technology and NFTs are transforming the gaming industry. Now, we turn our attention to a different facet of the blockchain landscape—enterprise blockchain development.
The Rise of Enterprise Blockchain Development
Blockchain technology has extended its reach far beyond cryptocurrencies and gaming. It is making a significant impact on the world of business and enterprise solutions. Enterprise blockchain development involves the application of blockchain technology to address specific industry challenges, streamline processes, enhance security, and increase transparency. In this article, we will delve into the world of enterprise blockchain development, exploring its use cases, benefits, and how businesses are harnessing the power of blockchain to transform various industries.
Understanding Enterprise Blockchain
Before we explore how blockchain is being used in enterprise solutions, let’s revisit the core principles of blockchain technology.
Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers, known as nodes. This decentralized structure eliminates the need for a central authority, making it resilient and resistant to censorship.
Transparency
All transactions on the blockchain are recorded in a transparent and immutable ledger. This transparency helps prevent fraud and ensures that data is trustworthy.
Security
Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure data. Once data is added to the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to alter or delete. This robust security is crucial for business applications.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined rules. They automate tasks when specific conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries.
Use Cases of Enterprise Blockchain Development
Enterprise blockchain development finds applications across various industries, solving complex problems and offering innovative solutions. Here are some notable use cases:
1. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain is transforming supply chain management by enhancing transparency, traceability, and accountability. By tracking the movement of goods from production to delivery on an immutable ledger, businesses can reduce fraud, improve product quality, and streamline logistics. For example, Walmart uses blockchain to trace the source of contaminated food quickly and efficiently.
2. Digital Identity Verification
Blockchain technology enables secure and efficient digital identity verification. Individuals can have control over their digital identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and enhancing privacy. Sovereign identity systems and self-sovereign identity projects are prime examples of blockchain applications in this area.
3. Cross-Border Payments
Traditional cross-border payment systems can be slow and costly. Blockchain-based solutions, such as Ripple’s XRP, are being used to facilitate faster and more cost-effective international money transfers for businesses.
4. Healthcare Data Management
Blockchain enhances the security and accessibility of healthcare data. Patients can have control over their medical records and share them securely with healthcare providers. This reduces administrative overhead and ensures the integrity of patient data.
5. Intellectual Property Protection
Blockchain can be used to protect intellectual property rights by securely timestamping and recording the creation of content, designs, or inventions. This is particularly valuable for artists, writers, and inventors.
6. Voting Systems
Secure and transparent voting systems can be built on blockchain technology. This ensures the integrity of elections and reduces the risk of fraud. Many countries are exploring blockchain-based voting systems.
7. Smart Contracts for Legal Agreements
Law firms and legal organizations use blockchain to create and enforce smart contracts that automate legal processes. These contracts reduce the need for intermediaries and enhance the efficiency of legal agreements.
8. Food Safety
Blockchain is used in food safety applications to track the production, transportation, and sale of food products. This ensures the safety and quality of the food supply chain.
9. Real Estate Transactions
Blockchain simplifies and secures real estate transactions by automating contract execution and title transfers. This reduces the risk of fraud and simplifies the buying and selling process.
10. Energy Trading
Blockchain is applied to peer-to-peer energy trading systems, allowing consumers to trade excess energy directly with each other. This can help reduce energy costs and promote sustainability.
Benefits of Enterprise Blockchain Development
The adoption of blockchain technology in enterprise solutions offers several key benefits:
Improved Transparency
Blockchain’s transparent ledger provides a single source of truth for all parties involved. This minimizes disputes and enhances trust among stakeholders.
Enhanced Security
The cryptographic nature of blockchain ensures data security and reduces the risk of unauthorized access and fraud. Data on the blockchain is immutable, making it tamper-resistant.
Streamlined Processes
Smart contracts automate complex processes, reducing the need for intermediaries and improving the efficiency of operations.
Reduced Costs
By eliminating intermediaries, businesses can reduce costs associated with transactions, compliance, and paperwork.
Increased Trust
The transparency, security, and immutability of blockchain data build trust among all parties in a transaction or process.
Global Accessibility
Blockchain technology operates on a global scale, enabling businesses to engage in cross-border transactions and operations more easily.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
To illustrate the impact of enterprise blockchain development, let’s look at a few real-world examples:
1. IBM Food Trust
IBM Food Trust is a blockchain-based solution that focuses on food safety. It allows retailers, suppliers, and consumers to trace the journey of food products from the farm to the store shelf. By enhancing transparency and traceability, IBM Food Trust improves food safety and reduces foodborne illnesses.
2. Walmart’s Blockchain Pilot
Walmart, one of the world’s largest retailers, has piloted a blockchain-based system for tracking and verifying the authenticity of pharmaceuticals. By utilizing blockchain, Walmart aims to enhance the security of its supply chain and ensure the legitimacy of products.
3. EY’s OpsChain
Ernst & Young (EY) offers a blockchain-based platform called OpsChain that streamlines supply chain management, procurement, and other operations. EY’s solution enhances transparency and efficiency, reducing costs for businesses.
4. V-ID’s Digital Document Verification
V-ID is a blockchain-based solution that provides secure document verification. It is used in various industries, including education, legal, and healthcare, to prevent document fraud and tampering.
5. Vechain for Luxury Goods
Vechain, a blockchain platform, is used to verify the authenticity of luxury goods, including wine and fashion items. It enables consumers to confirm the legitimacy of products by scanning QR codes.
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
While enterprise blockchain development offers significant advantages, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Integration Complexity: Integrating blockchain with existing systems and processes can be complex. A thoughtful transition plan is essential.
- Regulatory Compliance: Businesses must navigate the evolving regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology, especially in industries like finance and healthcare.
- Scalability: Scalability remains an issue for some blockchain platforms, leading to potential bottlenecks in high-transaction environments.
- Data Privacy: Balancing transparency with data privacy is crucial. Sensitive business data must be protected while maintaining the benefits of blockchain’s transparency.
- Network Security: The security of the underlying blockchain network is critical. Enterprises must take precautions to protect against network attacks.
- Education and Training: Staff and stakeholders may require education and training on blockchain technology to ensure successful adoption and operation.
Conclusion
Enterprise blockchain development is a dynamic field with vast potential for transforming traditional business practices. As we have seen, blockchain technology can address complex challenges in various industries, providing improved transparency, security, and efficiency.
DeFi Development: Building the Future of Finance
In our previous articles, we explored blockchain game development, web3-powered games, and the application of blockchain technology in enterprise solutions. Now, we venture into the dynamic and rapidly evolving world of decentralized finance (DeFi) development. DeFi represents a paradigm shift in the financial industry, where traditional financial services are being transformed into open, decentralized, and permissionless systems. In this article, we will delve into the realm of DeFi development, discussing the core concepts, benefits, popular use cases, and the role of smart contracts in reshaping the traditional financial sector.
Understanding Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance, often referred to as DeFi, is a collective term for various financial services and applications built on blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum. DeFi platforms aim to recreate traditional financial systems without intermediaries, such as banks or financial institutions. These platforms use smart contracts to automate and replace conventional financial intermediaries, providing a new level of financial inclusivity and control to users.
Core Concepts of DeFi
To understand DeFi development, it’s crucial to grasp the core concepts and components of this emerging ecosystem:
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined rules. They automate financial transactions and agreements when specific conditions are met. In DeFi, smart contracts play a central role in managing funds, providing liquidity, and executing complex financial operations.
- Liquidity Pools: DeFi relies on liquidity pools, which are decentralized reserves of assets used for trading and lending. Users provide liquidity to these pools in exchange for fees and rewards. Automated Market Makers (AMMs), like Uniswap and SushiSwap, are popular examples.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DEXs allow users to trade digital assets directly with one another without relying on centralized intermediaries. These platforms offer greater control over trading activities, reducing counterparty risk.
- Lending and Borrowing: DeFi platforms offer lending and borrowing services where users can provide assets as collateral and earn interest on their deposits. Borrowers can access funds by locking up collateral in a smart contract.
- Yield Farming and Staking: Yield farming involves locking assets in DeFi protocols to earn rewards, often in the form of native tokens. Staking involves holding and locking tokens to secure a blockchain network or participate in governance.
- Governance Tokens: Many DeFi platforms issue governance tokens that allow users to participate in the decision-making process of the protocol. Holders of these tokens can vote on proposals and changes to the platform.

Benefits of DeFi Development
DeFi development offers numerous advantages, which have contributed to its rapid growth and adoption:
- Accessibility: DeFi platforms are open to anyone with an internet connection, providing access to financial services for individuals who are excluded from traditional banking systems.
- Transparency: Transactions on the blockchain are transparent and verifiable. Users can inspect smart contracts and the movement of funds, enhancing trust in the system.
- No Intermediaries: DeFi eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks, which can reduce costs and minimize potential points of failure.
- Global Reach: DeFi is a global phenomenon, allowing users from anywhere in the world to participate in a borderless financial system.
- Liquidity: DeFi platforms provide liquidity for various assets, enabling users to easily trade, lend, and borrow without relying on centralized entities.
- Innovation: DeFi encourages innovation by enabling developers to create new financial products and services that were not possible within traditional finance.
Popular Use Cases in DeFi
DeFi development has given rise to a plethora of use cases, reshaping traditional financial services. Here are some of the most prominent DeFi applications:
1. Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap allow users to trade a wide range of tokens without intermediaries. Automated Market Makers (AMMs) use smart contracts to facilitate liquidity provision and trading.
2. Lending and Borrowing Platforms
DeFi lending platforms, such as Aave and Compound, enable users to provide assets as collateral and earn interest on their deposits. Borrowers can access funds by locking up collateral and paying interest.
3. Stablecoins
Stablecoins like DAI and USDC are digital assets with a stable value, often pegged to a fiat currency. They provide stability in a volatile cryptocurrency market and are commonly used for trading and lending.
4. Yield Farming and Staking
Yield farming involves locking assets in DeFi protocols to earn rewards, often in the form of governance tokens. Staking allows users to hold and lock tokens to participate in network security and governance.
5. Derivatives
DeFi has also seen the development of decentralized derivatives platforms, such as Synthetix, where users can create and trade synthetic assets representing real-world assets, commodities, or cryptocurrencies.
6. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are organizations run by smart contracts and governed by token holders. They allow users to participate in decision-making processes, make proposals, and vote on changes to the protocol.
7. Insurance
DeFi insurance platforms, like Nexus Mutual and Cover Protocol, offer users protection against smart contract vulnerabilities and other risks. Users can purchase coverage and earn premiums by providing liquidity.
8. Cross-Chain Solutions
Cross-chain platforms, such as Polkadot and Cosmos, aim to connect different blockchain networks, allowing assets and data to move seamlessly across chains.
DeFi Development Challenges and Considerations
While DeFi offers numerous benefits and opportunities, it also presents challenges and considerations for developers and users:
- Smart Contract Risks: Vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to security breaches and the loss of funds. Extensive testing and audits are crucial to mitigate risks.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The DeFi space is still evolving, and regulatory clarity varies by jurisdiction. Developers and users should be aware of potential regulatory challenges.
- User Education: DeFi platforms can be complex, requiring users to understand the risks and mechanics of various protocols. Proper education and user interfaces are essential.
- Scalability: Some DeFi platforms may experience scalability issues, leading to high gas fees and slower transaction times during periods of high demand.
- Market Volatility: DeFi assets are often highly volatile, and users should be prepared for price fluctuations.
- Counterparty Risk: While DeFi eliminates intermediaries, it introduces counterparty risk, as users interact directly with smart contracts and other users.
Case Study: Uniswap
Uniswap is one of the most successful and widely used DeFi platforms. It operates as a decentralized exchange, allowing users to swap various tokens without the need for a traditional order book or intermediary. The platform utilizes automated market makers (AMMs) to provide liquidity and enable decentralized trading.
Uniswap’s UNI token grants users governance rights, allowing them to propose and vote on changes to the protocol. The platform has significantly contributed to the growth of the DeFi ecosystem and has a strong community of users.
Conclusion
DeFi development is reshaping the traditional financial sector by offering innovative and decentralized solutions to users worldwide. With the use of smart contracts, liquidity pools, and decentralized governance, DeFi platforms are enabling open and permissionless access to a wide range of financial services. The benefits of DeFi, such as accessibility, transparency, and the removal of intermediaries, have driven its rapid growth and adoption.
Enterprise Blockchain Development: A Strategic Approach
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, blockchain has emerged as a disruptive force with the potential to transform various industries. While many have associated blockchain with cryptocurrencies, its applications extend far beyond digital assets. Enterprises, in particular, are recognizing the benefits of blockchain technology for enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency. This article explores the strategic approach to enterprise blockchain development, focusing on the key considerations, challenges, and opportunities that businesses need to address.
Introduction
Blockchain technology is often described as a distributed ledger that records transactions in a secure and immutable manner. It ensures trust and transparency through consensus mechanisms and cryptographic techniques. While blockchain’s roots lie in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its potential extends beyond the financial sector. In recent years, enterprises have started exploring the benefits of blockchain in various aspects of their operations.
Enterprise blockchain development involves creating tailored solutions to address specific business needs. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how businesses can strategically approach the implementation of blockchain technology to drive innovation, enhance security, and streamline processes.
The Case for Enterprise Blockchain
Before diving into the strategic aspects of enterprise blockchain development, it’s important to understand why businesses are showing interest in this technology. Several compelling reasons drive the adoption of blockchain in enterprise settings:
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic methods make it highly secure. Data stored on a blockchain is resistant to tampering and unauthorized access, providing an extra layer of protection for sensitive information.
- Transparency and Traceability: The transparent and immutable nature of blockchain ledgers ensures that all transactions are recorded and can be traced back to their origin. This feature is particularly useful in supply chain management, where tracking the source of goods is critical.
- Streamlined Processes: Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, automate processes, reducing the need for intermediaries. This leads to increased efficiency and cost savings.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries and streamlining processes, blockchain can significantly reduce operational costs. It can also expedite cross-border transactions, which typically involve multiple parties and significant delays.
- Compliance and Reporting: Blockchain can help organizations maintain compliance by recording and validating transactions according to regulatory standards. This simplifies the auditing process and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
- Innovation and Competitive Advantage: Being an early adopter of blockchain technology can give businesses a competitive edge. It allows them to explore new business models and stay ahead of industry trends.
- Global Collaboration: Blockchain enables secure, transparent, and efficient collaboration among multiple parties. This is especially beneficial in sectors where various stakeholders need to cooperate, such as international trade or healthcare.
With these benefits in mind, it’s evident that blockchain technology can be a game-changer for enterprises. However, to harness these advantages effectively, a strategic approach to blockchain development is essential.
Strategic Considerations for Enterprise Blockchain Development
Implementing blockchain technology within an enterprise requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some key strategic considerations for businesses embarking on an enterprise blockchain development journey:
- Define Clear Objectives:To begin, it’s crucial to define clear objectives for blockchain implementation. What specific problems or inefficiencies do you intend to address? This can range from supply chain optimization to reducing fraud, improving data security, or enhancing trust among stakeholders.
- Select the Right Blockchain Platform:There are various blockchain platforms available, including public, private, and consortium blockchains. The choice depends on the specific use case. Public blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin offer high security but limited privacy, while private blockchains provide more control but less decentralization. Consortium blockchains, on the other hand, are governed by a group of organizations.
- Design a Governance Model:Governance in the blockchain context refers to the rules, policies, and decision-making processes that define how the blockchain network operates. Establishing a governance model is crucial, especially in consortium blockchains, where multiple parties are involved. It ensures that all stakeholders have a say and that the blockchain operates as intended.
- Security and Privacy:Security is a paramount concern in enterprise blockchain development. Implementing robust security measures, including encryption and access control, is essential. Furthermore, businesses must carefully consider data privacy regulations, especially with the advent of GDPR and other data protection laws.
- Interoperability:Enterprises often rely on a variety of systems and technologies. Ensuring that the blockchain solution can seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure is critical. This may involve developing APIs and middleware to connect blockchain with legacy systems.
- Scalability:As an enterprise grows, so does the volume of transactions. Scalability is a critical consideration to ensure that the blockchain network can handle increased activity without compromising performance.
- User Experience:User-friendly interfaces and applications are essential for the adoption of blockchain within an enterprise. Employees, customers, and partners should find it easy to use and interact with the blockchain platform.
- Training and Change Management:Implementing a blockchain solution often requires a cultural shift within the organization. Training employees and stakeholders on blockchain technology and its benefits is vital. Change management strategies can help smooth the transition.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance:Understanding and adhering to relevant legal and regulatory frameworks is essential. Compliance with existing laws, such as data protection regulations and financial regulations, is crucial for avoiding legal issues.
Challenges in Enterprise Blockchain Development
While the benefits of enterprise blockchain development are substantial, there are also several challenges that businesses may encounter:
- Costs: Developing and maintaining a blockchain solution can be expensive. It’s essential to carefully assess the costs and potential returns on investment.
- Talent and Expertise: There’s a shortage of blockchain development talent. Businesses may struggle to find the right experts to build and maintain their blockchain solutions.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Integrating blockchain with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Regulatory frameworks for blockchain technology are still evolving. Businesses need to stay updated on legal developments and ensure compliance.
- Scalability Issues: As an enterprise’s blockchain network grows, scalability can become a challenge. Solutions must be designed to handle increased transaction volumes.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations like GDPR is critical.
Use Cases for Enterprise Blockchain
Enterprise blockchain has a wide range of use cases across various industries. Here are a few notable examples:
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track the origin and journey of products, ensuring authenticity and quality control. This is particularly valuable in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
- Financial Services: Blockchain is transforming the financial sector, from cross-border payments to trade finance and securities trading. It enhances security, reduces fraud, and speeds up transactions.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, blockchain can securely store and share patient records, ensuring data integrity and facilitating interoperability among healthcare providers.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent platform for electronic voting, enhancing the integrity of electoral processes.
- Intellectual Property: Blockchain can be used to prove ownership and protect intellectual property rights.
- Energy Trading: Decentralized energy grids can leverage blockchain for peer-to-peer energy trading and transparent billing.
Conclusion
Enterprise blockchain development represents an exciting opportunity for businesses to leverage the benefits of this transformative technology. To succeed, a strategic approach is vital, involving clear objectives, the selection of the right blockchain platform, robust governance models, and an understanding of the challenges and use cases.
Leave a comment